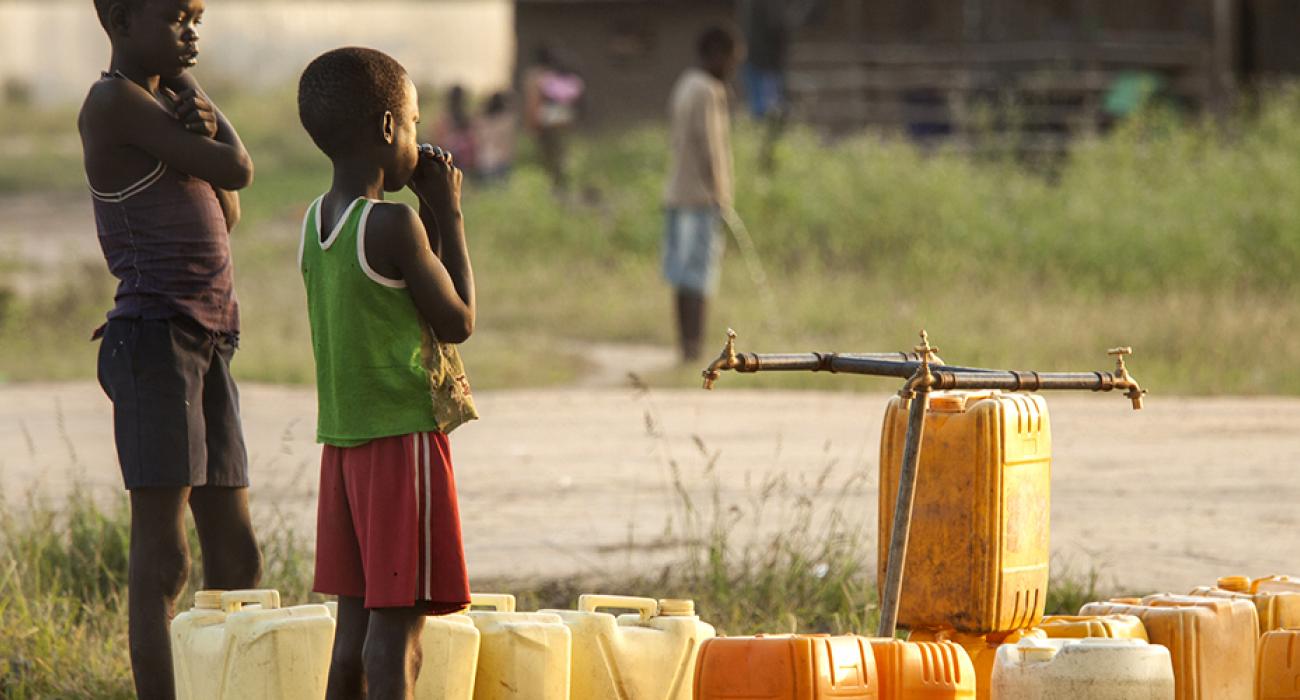
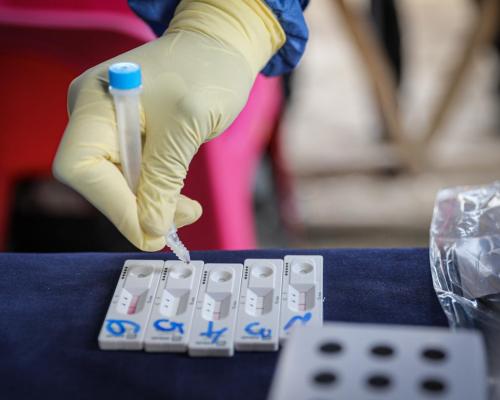
Cholera is an infectious disease that causes severe watery diarrhoea, and can lead to dehydration and kill within hours if left untreated. People with low immunity – such as malnourished children or people living with HIV – are at a greater risk of death if infected.
The symptoms of cholera include diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting, and severe dehydration. Diarrhoea due to cholera often has a pale, milky appearance that resembles water in which rice has been rinsed, also known as rice-water stool.
The signs and symptoms of cholera in children are similar to adults but they may also experience fever, extreme drowsiness, convulsions or even coma. Only about 1 in 10 infected people develop the typical signs and symptoms of cholera, usually within a few days of infection.
The disease is most common in places with poor sanitation, urbanization, conflict zones and famine. Effective ways to protect yourself is using water that has been boiled, water that has been chemically treated, or bottled water.